Plastics in relation to lifetime of lithium-ion batteries
Battery construction in an electric car. What properties do lithium-ion batteries have? Expanded polypropylene EPP as battery insulation.
Electric car manufacturers usually choose lithium-ion (Li-Ion) batteries as they allow them to travel longer distances compared to other technologies. Although in this case there is no memory effect and a lifetime of such car batteries is long, they should be operated under appropriate conditions.
Lithium-ion batteries were first used to power cameras in the early 1990s and have been spreading rapidly since then. Their considerable advantage in comparison to hydride or nickel-cadmium batteries is a higher energy density. This means that they are able to store more energy for every kilogram of cell. Moreover, this technology still has significant development potential – it is estimated that this type of batteries will be able to store two or three times as much energy, up to 300-350 Wh/kg in a decade.
At the same time, they are relatively cheap to produce. Lithium-ion batteries are very durable and long-lasting, but unfavourable operating or storage conditions can shorten their lifetime or even lead to their failure. They are particularly sensitive to extreme temperatures, against which they are protected by modern car cooling systems and components made of innovative expanded polypropylene (EPP) insulation foams.
How do lithium-ion batteries work? Battery construction in an electric car
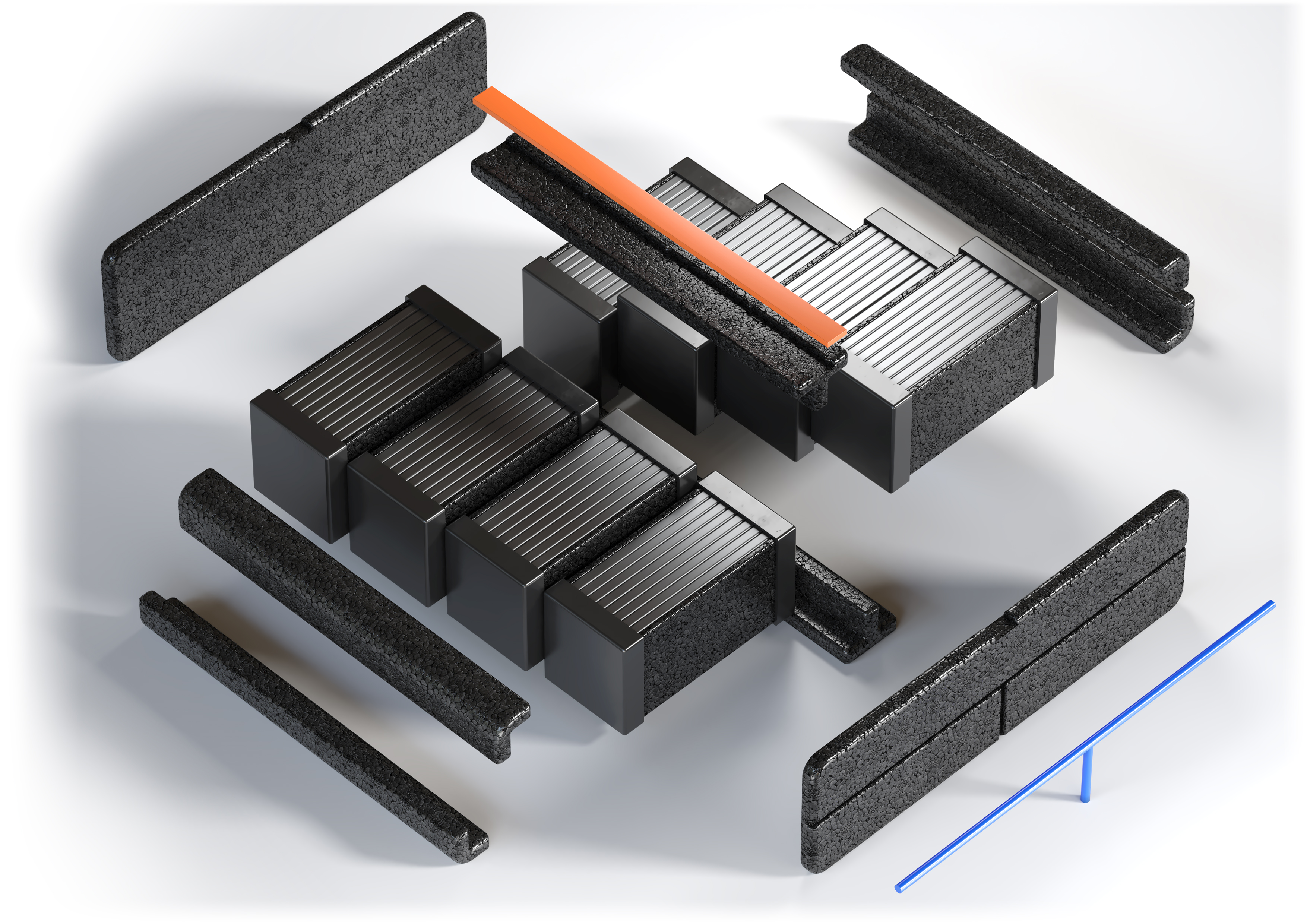
Lithium-ion cells used in electric car batteries have two electrodes – positive and negative. They are separated by an electrolyte in the form of liquid, gel or solid, which function is to transfer charges between them. Lithium-ion batteries available on the market may vary in chemical composition and design; however charge carriers are always lithium ions. Their manufacturers are still working on increasing energy density, widening the range of operating temperature, shortening the charging time and, above all, improving operational safety.
The aim is to prevent an excessive increase in the temperature of the electrolyte, which is prevented by special additives, active cooling systems in the car or innovative insulators used in battery construction. In order to prevent potential danger, instead of large batteries, electric cars are equipped with stacks of up to several thousand small cells, which are isolated from other components. In this way, even if one of them malfunctions, there is no further heat emission or short circuits between the individual cells. The stacks are also installed in the cars in a way which minimizes their exposure to damage.
Read more: Types of electric car batteries – which one is the best?
How to extend the battery life in an electric car?

Battery life in electric cars is generally estimated to be 10 years, giving about 2500-3500 charging cycles. Depending on the technology used and the way it is used, the lifetime may be even longer. Firstly, the battery should not be allowed to discharge completely. The car draws energy not only while driving but also at a standstill. A several-month standstill may even result in damage to the battery, which is why it should also be charged from time to time.
On the other hand, a lithium-ion battery should not be charged to 100%. The recommended battery charge level is in the range of 20-80%. The health of a battery is ideally affected by low-power charging. The use of a high-power electric car quick charging station shortens battery life.
Another important factor is temperature – both heat and cold have a negative impact on the condition of a lithium-ion battery. Permissible temperature range of their operation is from 0 to 45°C, the latter value should not exceed 30°C. That is why the insulating materials used in the battery construction are so important for its condition. Among the very promising ones is expanded polypropylene EPP, which is already used today both as a raw material for the production of protective packaging for batteries and insulation components in battery packs.
Expanded polypropylene – innovative battery insulation
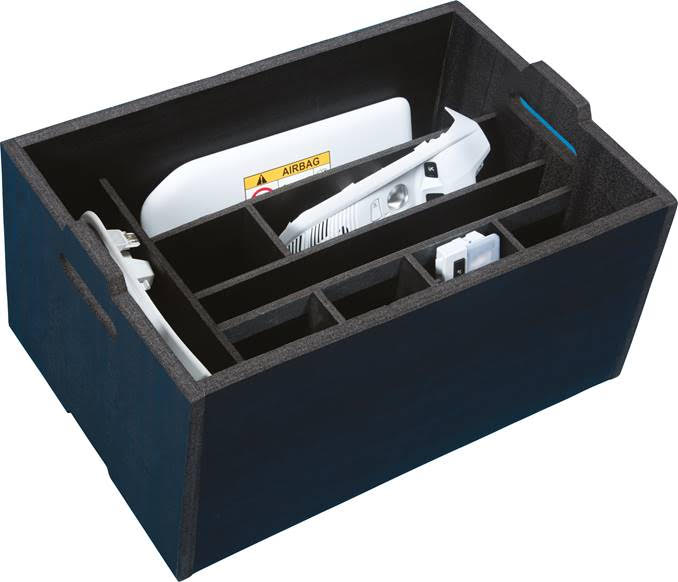
Lithium-ion batteries used in cars are sensitive to both thermal and mechanical factors, so they must be stored, transported and operated under conditions ensuring their longest possible lifetime. A material which has proved particularly effective in all these applications is expanded polypropylene (EPP). It is perfectly suited for the production of battery transport packaging, as it has excellent thermal insulation properties and effectively protects the contents from mechanical damage.
Komebac® packaging adapted to the requirements of the automotive industry can be customised to the shape and dimensions of lithium-ion batteries in every respect and have special protective inserts. In this way the batteries are 100% protected – not only against the penetration of extreme temperatures during transport, but also against moisture and shocks. The material absorbs impacts perfectly, does not crumble or deform. Thanks to all of this, it is now used in the manufacture of batteries, as a raw material for the manufacture of automotive battery packs. It is currently used for the production of battery cell separators, special insulations and fastening rails. EPP foam is also an excellent electrical insulator, which effectively prevents uncontrolled current flow between cells, and battery failure.
Watch the video about the production process of lightweight automotive components from Expanded Polypropylene (EPP)